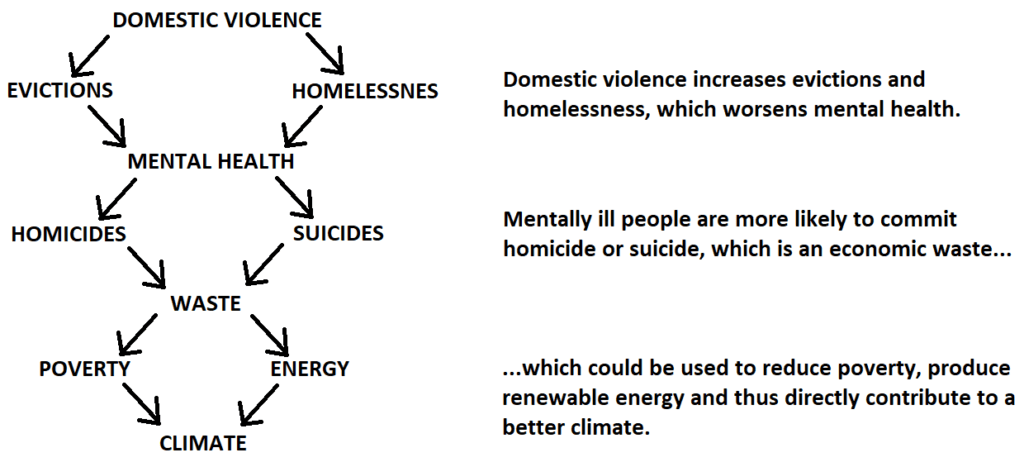
Domestic violence is not only a private but also a public problem because it affects many other problems. However, as it happens behind closed doors, we can easily call it a “silent killer.” Here is just a few facts:
Mental Health
On average, more than half of the women seen in mental health settings are being or have been abused by an intimate partner. There are specific diagnoses that are commonly experienced by these women: post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and anxiety.
Physical Health
1 in 7 women and 1 in 18 men have been stalked by an intimate partner during their lifetime to the point in which they felt very fearful or believed that they or someone close to them would be harmed or killed. About 41% of the female survivors and 16% of male survivors are physically injured as a result of domestic violence. Only 34% of people who are injured by intimate partners receive medical care for their injuries.
Suicides
Suicide and intimate partner violence are both major public health crises, and they’re closely linked. Survivors of intimate partner violence are twice as likely to attempt suicide multiple times and cases of murder-suicide are most likely to occur in the context of abuse. Domestic victimization is correlated with a higher rate of depression and suicidal behavior.
Homelessness
Domestic violence is a leading cause of homelessness for women and their children. Many victims face homelessness when they flee abusive homes. 28% of families were homeless because of domestic violence and 39% of cities cited domestic violence as the primary cause of family homelessness.
Homicides
A study of intimate partner homicides found that 20% of victims were not the intimate partners themselves, but family members, friends, neighbors, persons who intervened, law enforcement responders, or bystanders. 72% of all murder-suicides involve an intimate partner; 94% of the victims of these murder suicides are female. The presence of a gun in a domestic violence situation increases the risk of homicide by 500%.
Incarceration
Intimate partner violence accounts for 15% of all violent crime. A felony domestic violence offense can lead to up to 5 years in state prison. Probation could also be as long as 5 years. There is a minimum of 3 years of probation as a state requirement in all cases of felony domestic violence.
Economic Loss
Intimate partner violence is estimated to cost the US economy between $5.8 billion and $12.6 billion annually, up to 0.125% of the national gross domestic product. The most recent estimates of public costs associated with IPV exceed $8 billion annually, including more than $1 billion associated with life lost.
Poverty
Families who experience domestic violence are often also victims of poverty. Research shows that a variety of factors may contribute to the poverty of women and children who have experienced domestic violence, including lack of affordable housing and lack of accessibility to legal assistance. Some of the most significant factors are barriers to employment. These employment barriers can lead to tardiness, absenteeism and lack of productivity. Research shows that between 23% and 42% affected by domestic violence report that the abuse had an impact on their work performance.

In addition to the issues mentioned, domestic violence has a direct and indirect impact on a number of other problems such as evictions, housing, hunger, etc.


